We are now going to practice using JavaScript to solve simple problems, to check we understand some of the fundamentals of the language before we start getting into more complicated code. We are also going to get some experience of using testing frameworks to check our code is correct.
We have a set of code templates to work from this week. Download the starting source code for this week and extract it.
There are a lot of files in this folder.
- There are a number of
.jsfiles. Each one contains a single JavaScript function that we need to complete. - There is a folder called
test. This contains test cases that check that the JavaScript functions we are going to write are working correctly. - There is a
.gitignorefile. This tells Git to ignore certain files and folders and not to include them in the repository. - There is a
package.jsonand apackage-lock.json. These are used for managing the installation of JavaScript modules when we are using JavaScript on the command line. We’ll look at these in more detail in a couple of weeks time.
Open a command line, and navigate to the directory with all the files you just downloaded. The first thing we need to do is install some requirements for todays lab. We can do this using the command npm install. This will download a few JavaScript packages into a folder called node_modules. You don’t need to worry about this too much at the moment, again, we’ll look at this more in a couple of weeks time.
As mentioned - the code we have downloaded comes with a set of test cases that check whether the code is working. We can run these tests with the command npm test. If you run this command, you should see the output from all the tests included in the test directory. There will be a lot of errors, because at this point all but one of our tests are failing.
It’s difficult to see what’s going on when we run all the tests at the same time, so let’s run an individual test instead:
npm test test/test_hello.jsYou should get some output something like the below:
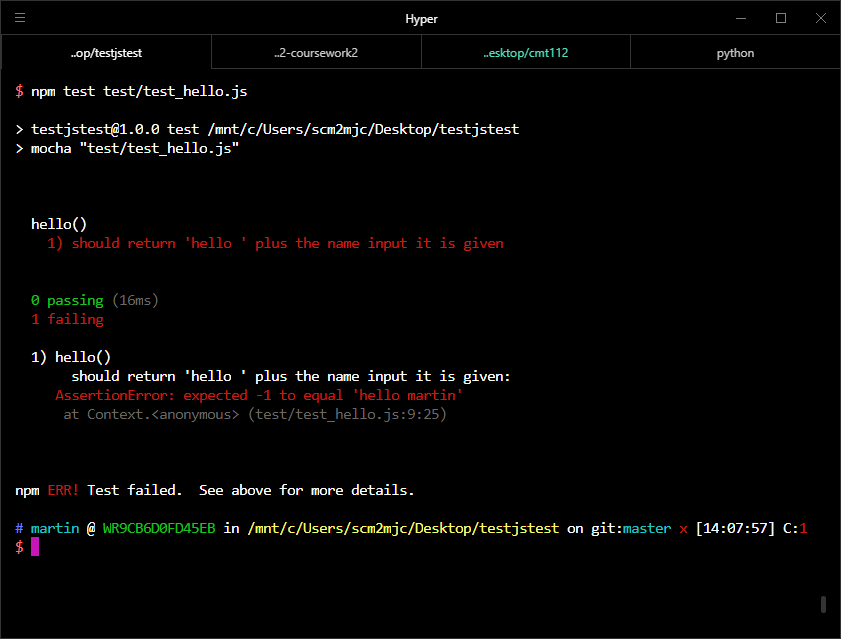
This command has run the test case in the file test_hello.js, which checks the function in hello.js to make sure it works correctly. The test is failing, so clearly there is something wrong with our function. Open up the file hello.js
function hello(name) {
// should return "hello name"
return -1;
}
module.exports = hello;We can see that the function hello just returns -1, when it should use the name it is given and return a String. Let’s fix the function:
function hello(name) {
// should return "hello name"
return "hello " + name;
}
module.exports = hello;If we save the file, and then run the test again:
npm test test/test_hello.jsWe should see that we have fixed the code and the test case now passes:
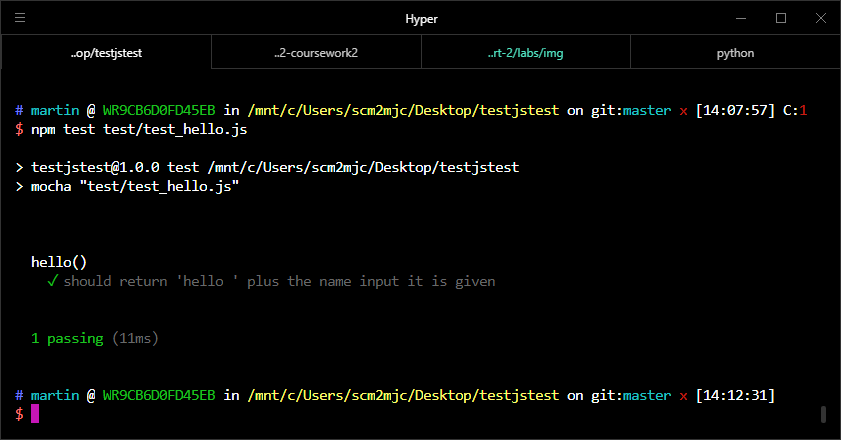
Your task for this week is to go through the JavaScript functions fixing them so that they all pass their test cases. At the end of the session you should be able to run npm test and get no error messages about failing tests. Each time you complete an exercise, submit your working code to the form here
The problems
1.) Hello
- file:
hello.js - test:
test/test_hello.js
This function accepts a String as input and should return that String with hello prepended to it.
2.) Sumall
- file:
sumall.js - test:
test/test_sumall.js
This function accepts a number as input. It then returns the sum of all numbers lower than or equal to this value. For example, if given the input 5, it should return 15 - (5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1)
3.) Sumall35
- file:
sumall35.js - test:
test/test_sumall35.js
This function accepts a number as input. It then returns the sum of all numbers lower than this value that are exactly divisible by 3 or 5. For example, if given the input 7, it should return 14 - (6 + 5 + 3)
4.) Largest
- file:
largest.js - test:
test/test_largest.js
This accepts an Array as input and should return the largest value in the Array. For example, if given the input [4, 3, 2] it should return 4
5.) HighestLowest
- file:
highestlowest.js - test:
test/test_highestlowest.js
This function accepts a String as input. This String will be a set of space separated numbers. The function should return the highest and lowest numbers in the String, as another space separated String, with the highest number first. For example, given the input "4 6 8" it should return "8 4"
6.) Even Or Odd
- file:
evenorodd.js - test:
test/test_even_or_odd.js
This function takes a number as input and returns “even” if the number is even (exactly divisible by 2) or “odd” if the number is odd.
7.) MakeNegative
- file:
makenegative.js - test:
test/test_makenegative.js
This function takes a number as input. If the number is positive, it returns a negative number with the same magnitude. If the number is negative, it returns the number. So, for example, given the input 5 it should return -5
8.) Middle
- file:
middle.js - test:
test/test_middle.js
This function takes a String as input. If the length of the String is odd, it returns the middle character of the String. If the length of the String is even, it returns the middle two characters.
9.) Mumbling
- file:
mumbling.js - test:
test/test_mumbling.js
This function accepts a String as input and returns a new String made up of the characters of the original string repeated n times, where n is their position in the original String. The set of repeated characters should be in TitleCase. For example, given the input her it should return H-Ee-Rrr
10.) Palindrome
- file:
palindrome.js - test:
test/test_palindrome.js
This function returns true if the supplied input String is a palindrome, false if not. A palindrome is a word that is spelt the same backwards and forwards.
11.) Repeat String
- file:
repeatstring.js - test:
test/test_repeatstring.js
This function accepts a String s as input and a number n and returns the String s repeated n times. For example, if given the input hi and 6, it would return hihihihihihi
12.) Smush
- file:
smush.js - test:
test/test_smush.js
This function accepts two Arrays as inputs, and returns a new array formed by stitching the two Arrays together an element at a time. For example, given the input [5, d] and [f, 6] it should return [5, f, d, 6]
13.) Population
- file:
population.js - test:
test/test_population.js
This function models population growth to see how long it will take a town of a certain size to reach a target population. It has a number of parameters:
- the starting population
- the natural percentage increase each year
- the number of people who move to the town each year
- the target population
The function will use the first three parameters to calculate and return the number of years before the population hits the supplied target.
Previous: Objects